Featured articles
Science writing & reporting
University of Cambridge, Researchers redesign future mRNA therapeutics to prevent potentially harmful immune responses
MRC Toxicology Unit, Mitochondrial damage: the missing piece in understanding the side-effects from antipsychotics?
MRC Toxicology Unit, Tracing toxic ‘tyre dust’ pollution in the air to assess human exposure
MRC Toxicology Unit, ‘Ageing’ immune cell levels could predict how well we respond to vaccines
MRC Toxicology Unit, People with obesity lose immunity gained from COVID-19 vaccination more rapidly
MRC Toxicology Unit, Cells build local supply chain of metabolites required for gene expression regulation
Excursions Journal, How Science Communication Helped Me Find my Identity as a Scientist
Imperial College London, How can we build a better balance of women in STEM?
AssayGenie, Metabolism of pluripotency – which regulates which? A chicken or the egg story.
MRC London Institute of Medical Sciences, Hunting for the truth amongst the noise: lessons from single cells
MRC London Institute of Medical Sciences, Tumours induce muscle wasting to fuel their growth
MRC London Institute of Medical Sciences, Plants ‘feel the glow’ when using mushroom genes
MRC London Institute of Medical Sciences, Short and sweet: the life of thirsty flies on sugar-rich diets
MRC London Institute of Medical Sciences, Hodor ‘holds the door’ open for a potential new way to curb mosquito populations
MRC London Institute of Medical Sciences, Don’t lose heart, it’s a promising future for AI in cardiac imaging
MRC London Institute of Medical Sciences, An Elegan(t) screen shows how the microbiome improves drug efficacy
MRC London Institute of Medical Sciences, New insights into how blood vessels control bone formation
MRC London Institute of Medical Sciences, AI analysis learns to predict survival from the movement of your heart
MRC London Institute of Medical Sciences, Hunting for the truth amongst the noise: lessons from single cells
Signal to Noise magazine, Stem Cell Dentistry: Revolutionizing Visits to the Dreaded Dentist’s Chair
Science communication articles
Short form writing

Breast Case Scenario
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in the UK, accounting for 15% of all new cancer cases. If breast cancer is spotted earlier, then the patient’s chances of survival dramatically increase. Mammograms are a well-known way that medics can detect and measure breast density and spot any cancers that may be starting to form. But this analysis is done manually so it can be misinterpreted, different doctors may have varying opinions, it is time consuming and the poor image quality makes small changes difficult to spot with the naked eye. In order to try and make critical diagnoses earlier, researchers applied a machine learning model to analyse mammography images to improve the detection and classification of benign (left) and malignant breast tumours (right), which the model did with incredible accuracy. It was a promising performance that helps the clinician with speedy diagnosis, treatment planning, and follow-up of disease progression.
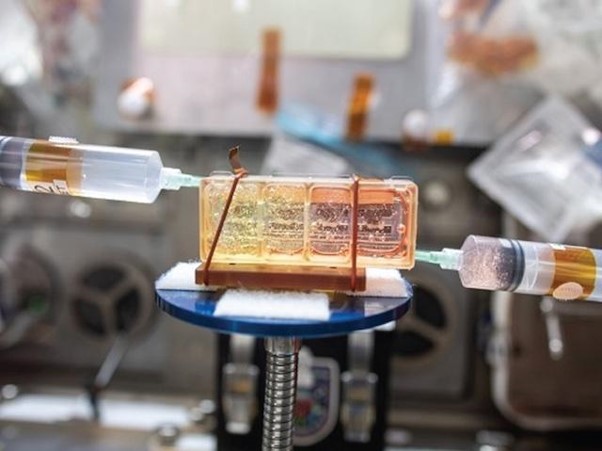
Outta This World
Stem cells hold much hope for medicine as they can become a range of different cell types. Researchers in labs across the globe are studying the biology of these specialised cells and testing ways to turn them into cardiac cells to treat heart conditions, for example. All this hype, but one major obstacle stopping such therapies becoming more commonplace is efficiently producing large batches of cells to use. One potential solution to this is travelling 250 miles above us on the International Space Station. This unique lab allows astronauts to perform experiments in microgravity and these near-zero gravity conditions may hold the secret to rapid mass production of stem cells for regenerative medicine. Astronauts are also working on projects to engineer stem cell-derived products like cardiac tissue (pictured) and model diseases which could form a futuristic roadmap of biomanufacturing to bring us new ways to live healthier lives.